Software Project: Process Mining (WIP)
Table of Contents
Introduction
📦 Initial Situation
As part of an SAP S/4HANA migration, I focused on improving business processes. The central question was how the new ERP system could positively influence existing workflows.
One key challenge was achieving reliable results quickly with limited resources. My specific task was to transition the picking warehouse from a fixed-location storage system to a chaotic (random) storage approach.
However, the analysis showed that an isolated change in warehouse strategy would not provide a sustainable solution in the context of a system conversion. Instead, the focus shifted toward a holistic view of end-to-end processes.
To develop a robust and flexible solution, I decided to align closely with common industry standards and integrate them as an “overlay solution.” This ensures independence from specific vendor products (such as SAP Signavio) while enabling internal benchmarking: in-house processes can be compared with those offered by IT service providers, allowing a realistic assessment of their actual added value.
This project is also based on open-source technologies to provide a sustainable, non-proprietary, and auditable analytics solution. This approach helps avoid vendor lock-in, allows better control over costs and update cycles, ensures transparency of algorithms and data flows, and improves adaptability to changing processes and S/4HANA releases.
Because of the need to establish data and KPI governance, integrate multiple source systems, and iteratively improve processes, the initiative is designed as a multi-year program: starting with piloting (discovery/conformance) in core processes, followed by performance analysis and KPI monitoring, and later scaling to additional areas with automation, benchmarking, and continuous optimization.
🎯 Objectives (High-Level)
A centralized interface (MUI) for process analysis and optimization:
| Phase | Feature |
|---|---|
| 0 | Process Discovery The interface automatically extracts as-is processes from event logs and visualizes them clearly. This creates transparency about real process flows, including variants and deviations. Users can immediately see how processes actually run—independent of target models or assumptions. 🔍 Transparency 🌐 Identify variants 📊 Build a factual basis |
| 1 | Conformance Checking The interface compares as-is processes with target models. Deviations are automatically identified and visualized so that rule violations, workarounds, or inefficiencies become immediately visible. ✅ Ensure compliance ⚖️ Verify process integrity 🚦 Improve process quality |
| 2 | Extension The interface enriches process models with additional information such as lead times, resource utilization, and bottlenecks. Dashboards present relevant KPIs, while predictive analytics provide forecasts of potential delays or risks. ⏱️ Measure performance 🧭 Identify bottlenecks 🔮 Predict risks |
| 3 | Process Improvement The interface supports active process optimization, including simulations (“what-if” scenarios), automated improvement suggestions, and comparisons with best-practice models. This allows for iterative redesign and sustainable optimization of processes. 🛠️ Adjust processes 🎯 Simulate optimizations ♻️ Continuously improve |
Motivation and Problem Definition
Requirements
Functional Requirements
Non-Functional Requirements
System and Project Planning
Project Organization
Milestones
Resources
Technologies Used
Languages: Rust, TypeScript, JavaScript
Frameworks: React, Zustand, MUI, Tauri
Databases: NoSQL, HANA
Risks
Analysis and Design
Warehouse Strategies
Zoning Concept
The warehouse space was divided into functional zones, for example:
| Zone | Purpose | Relevant Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| High-Runner Zone | Fast access to frequently used items | ABC analysis, FIFO, Slotting |
| Hazardous Materials Zone | Safe storage of legally regulated goods | Storage class control, access control |
| Quality Inspection Zone | Incoming goods inspection | Quarantine and inspection storage strategy |
| VAS Zone | Value-Added Services (kitting, labeling) | Workstation-oriented control |
| Picking Zone | Pick & Pack / Multi-Order Picking | Picking strategy |
| Supply Zone | Just-in-time material supply | Kanban, replenishment |
Note: The chaotic warehouse strategy is deliberately applied within specific zones to optimize flexibility and utilization.
🖼️ Demo
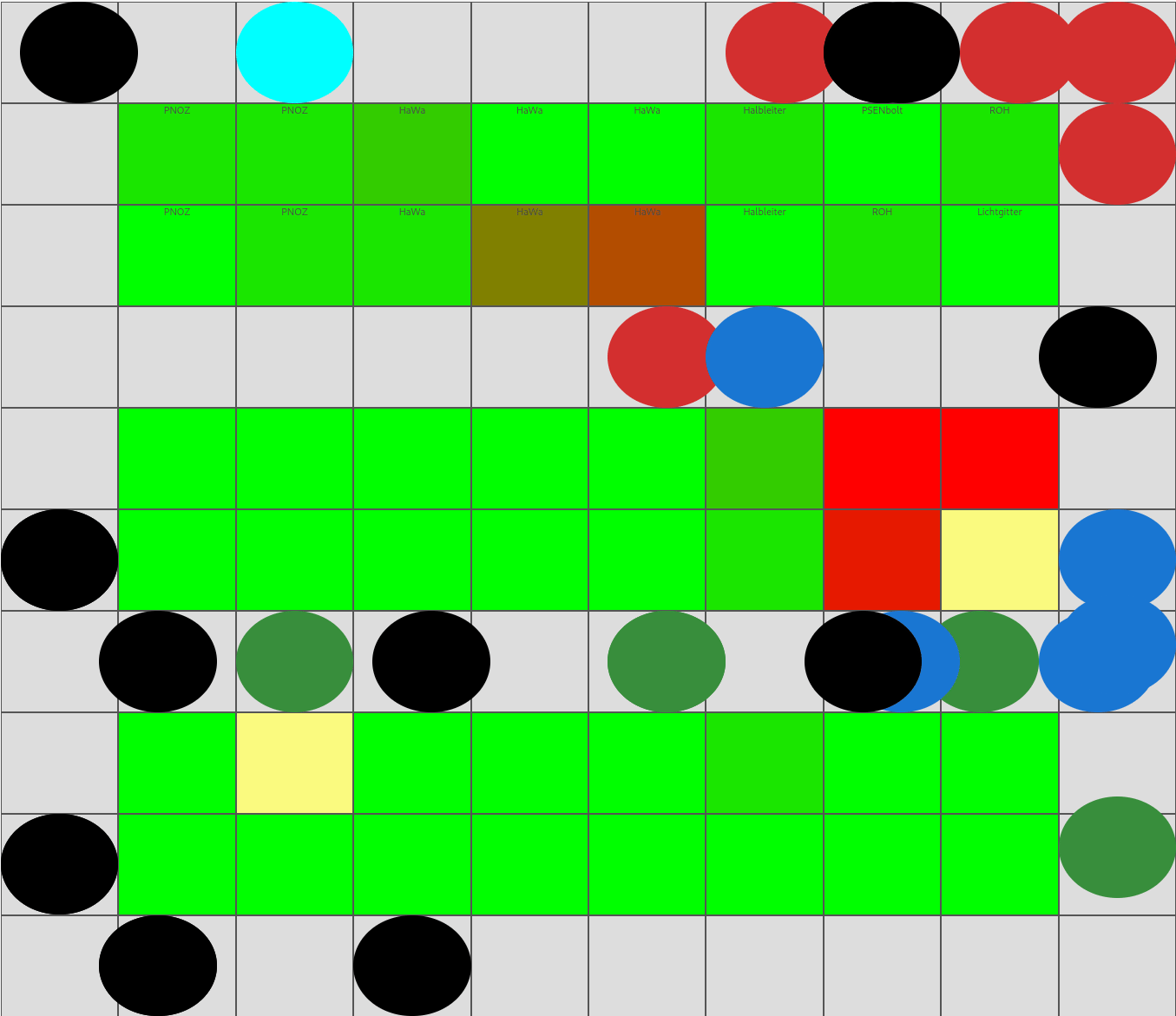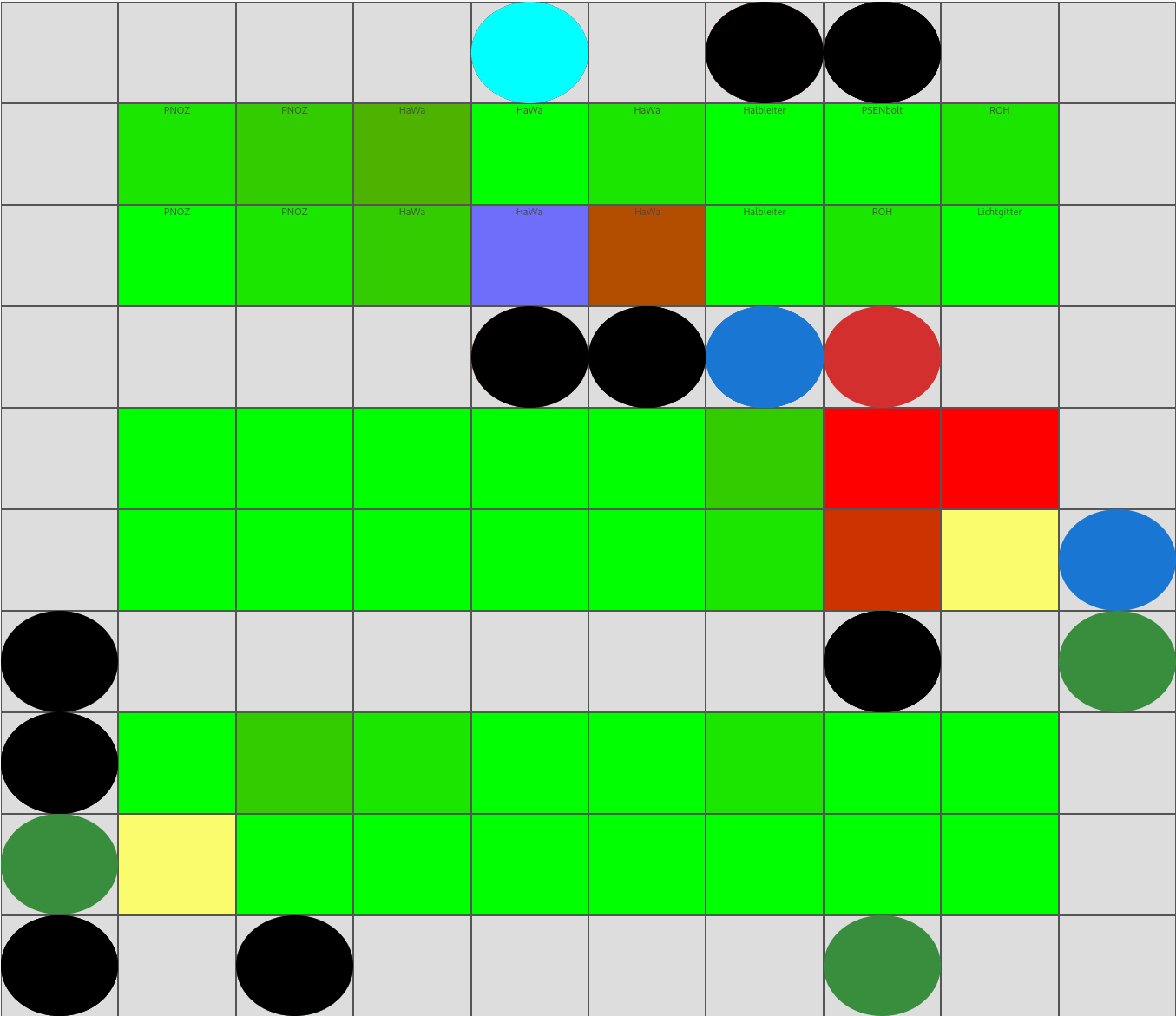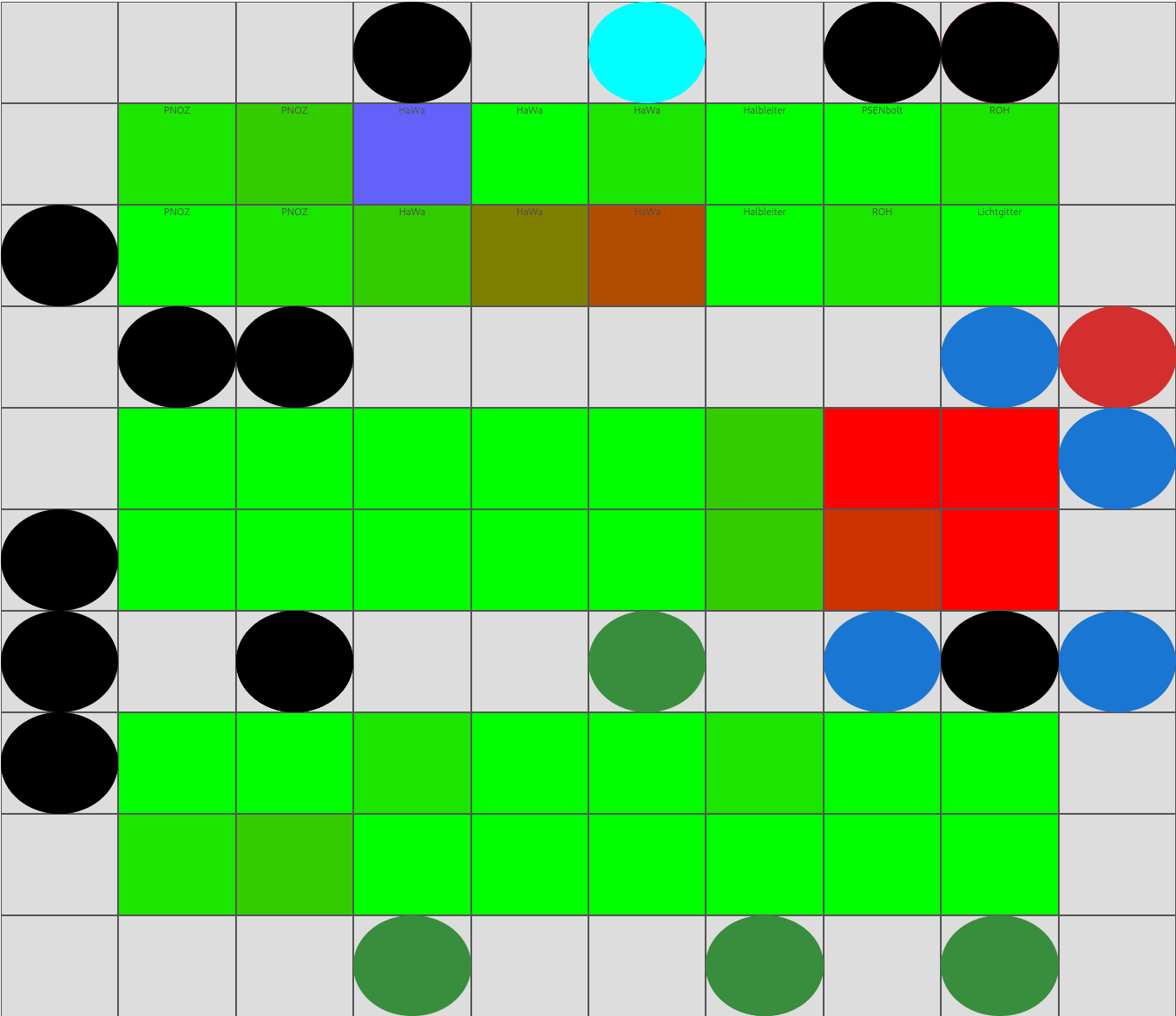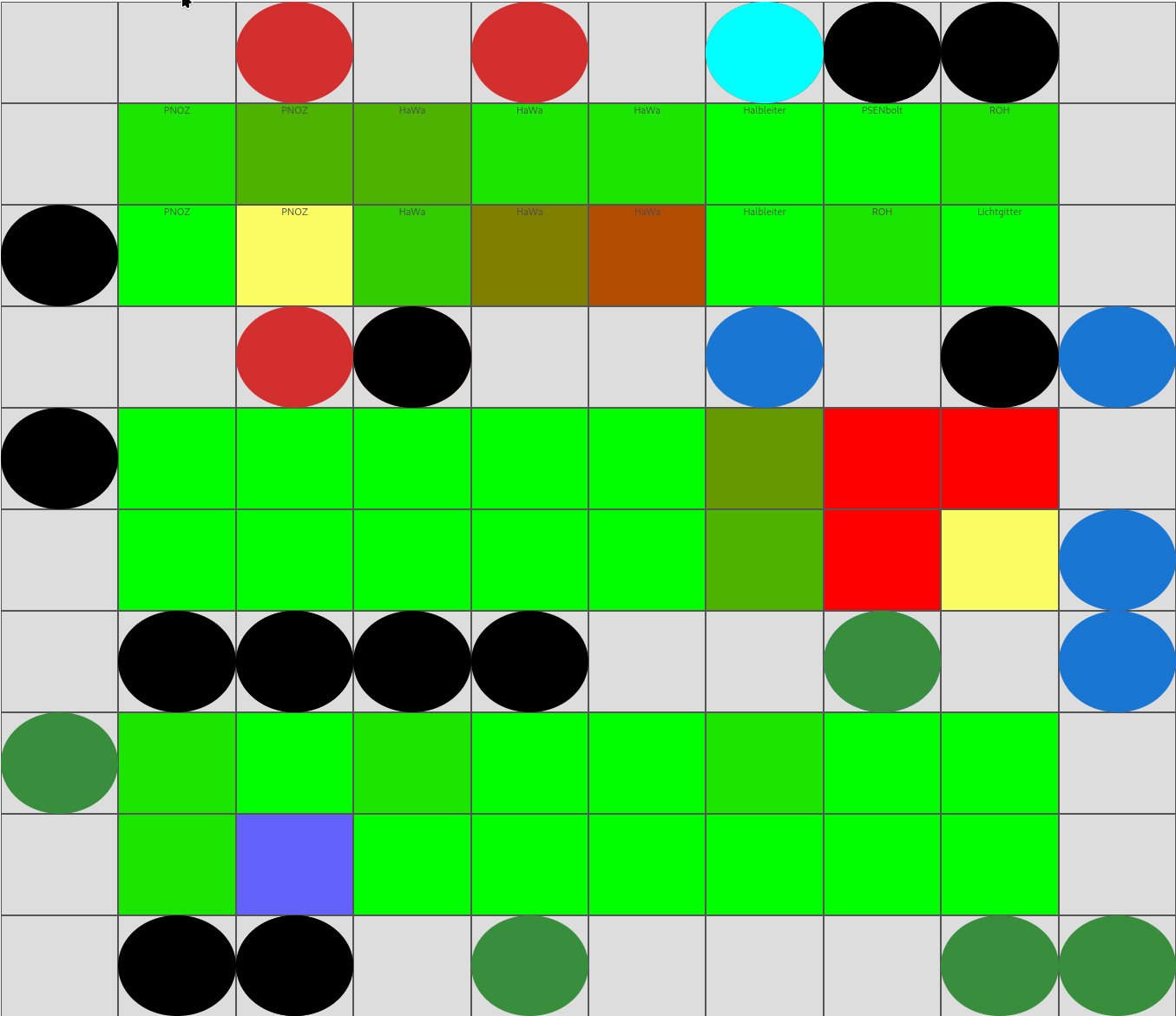
Programmatic view of warehouse picking utilization
The demo illustrates how dynamic warehouse strategies can improve utilization and warehouse KPIs.